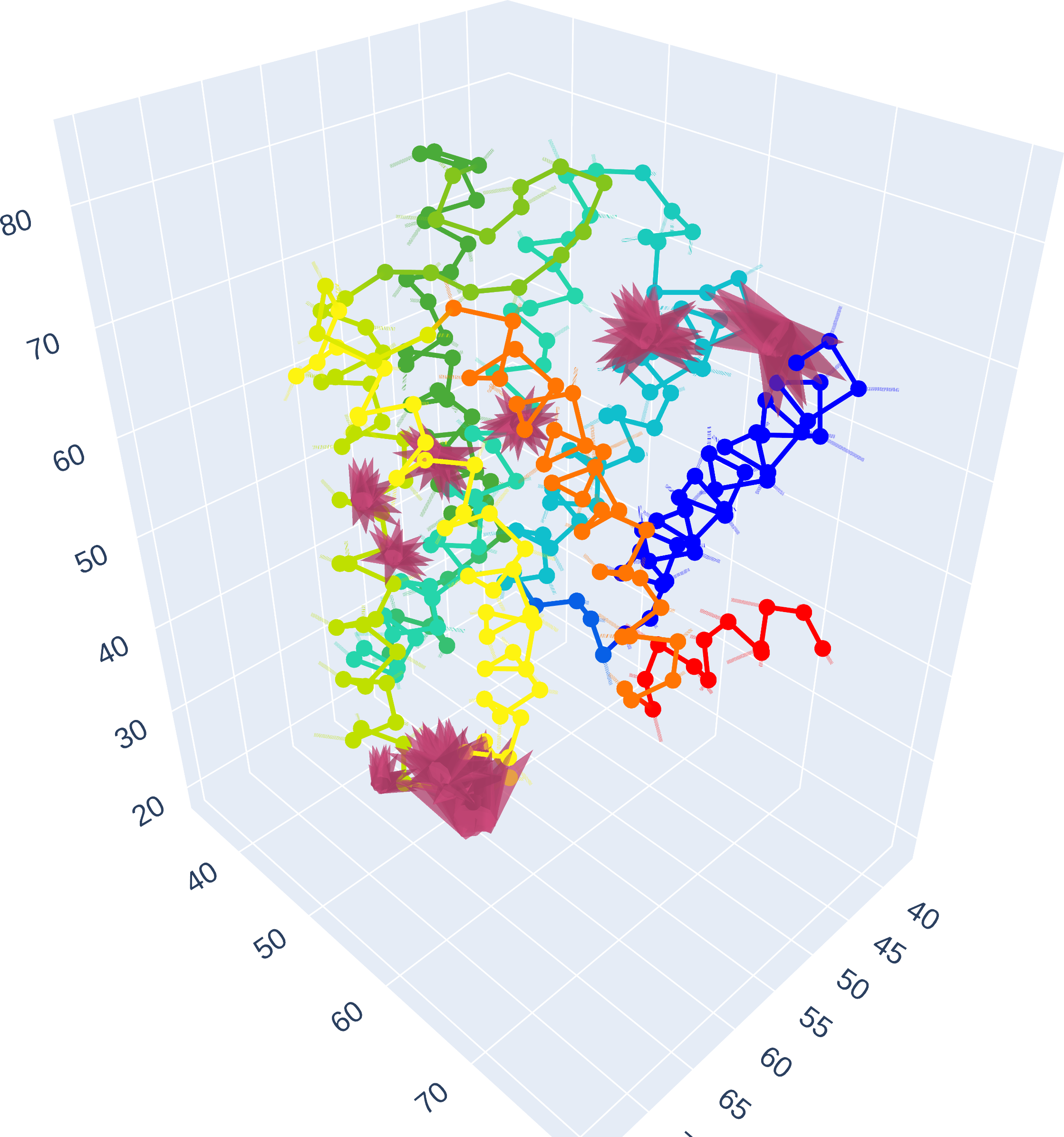
We trained models to predict whether the 5HT2A receptor was bound to psilocin (psychedelic) or 5-HT (non-psychedelic), but the model could only use the 5HT2A receptor structure as its input. Once these models were able to accurately predict the "psychedelicness" of the receptor, we employed interpretability methods (saliency scores) to investigate significant residue interactions that influenced the model's correct decision-making.
5HT2A - Residue Interactions
CLICK ON IMAGE FOR INTERACTIVE REPRESENTATION
Especially noteworthy is the attention paid to the interactions with the 3.36 residue, whose mutation has been found to drastically reduce 25NBOH potency [3]
Furthermore, we observe a focus on 6.52, which has been identified to play an important role in 5-HT2a receptor activation by N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists [2]
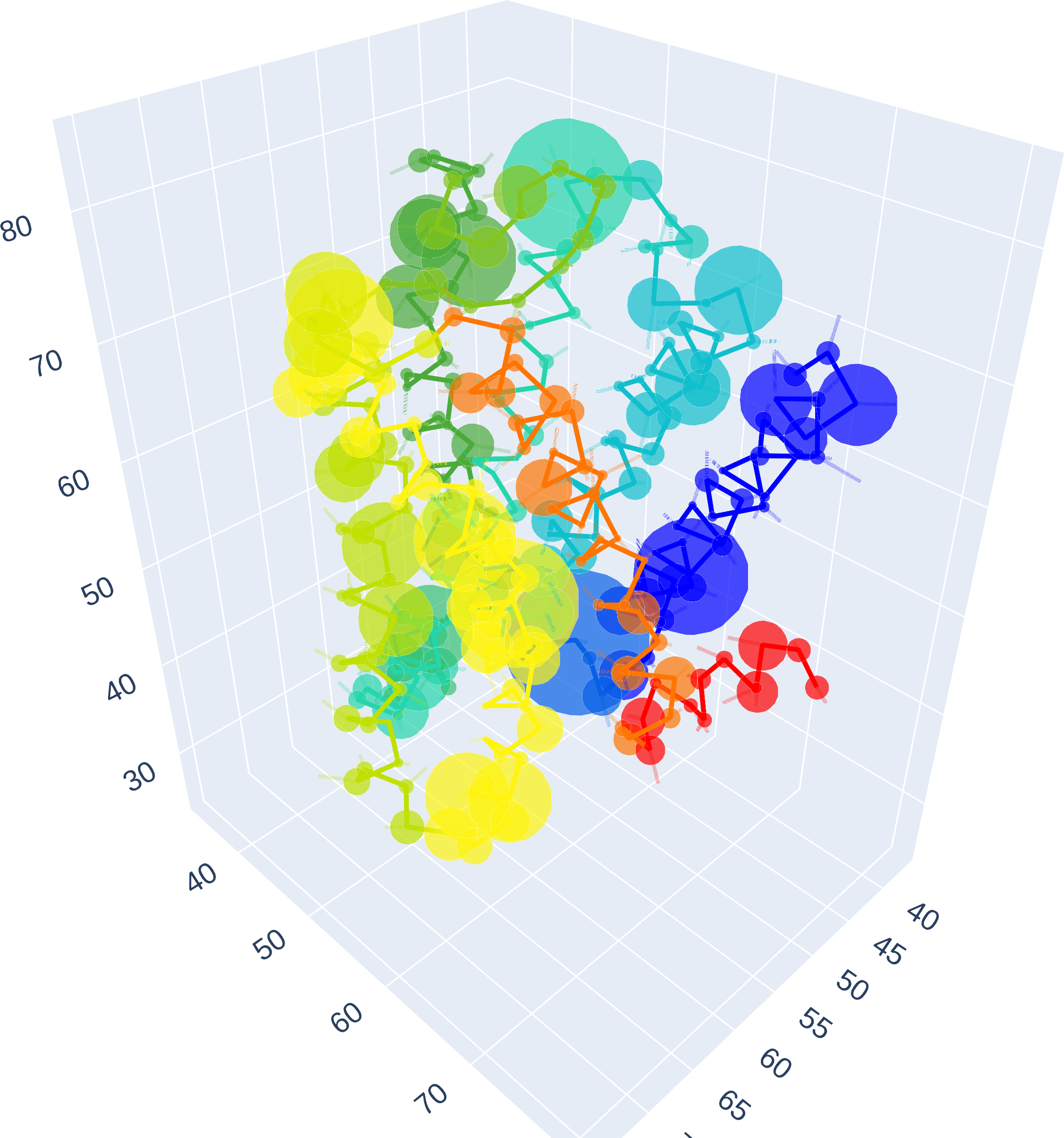
5HT2A - Residues
CLICK ON IMAGE FOR INTERACTIVE REPRESENTATION
Interestingly, the model pays a lot of attention to residue 185, whose mutation has been found to significantly reduced the efficacy of 25CN-NBOH [3]
Also strong focus on 6.44 and 5.50, which are of PIF motif and have been found to play a pivotal role in hallucinogen-activated 5HT2A receptor structures as well [3]
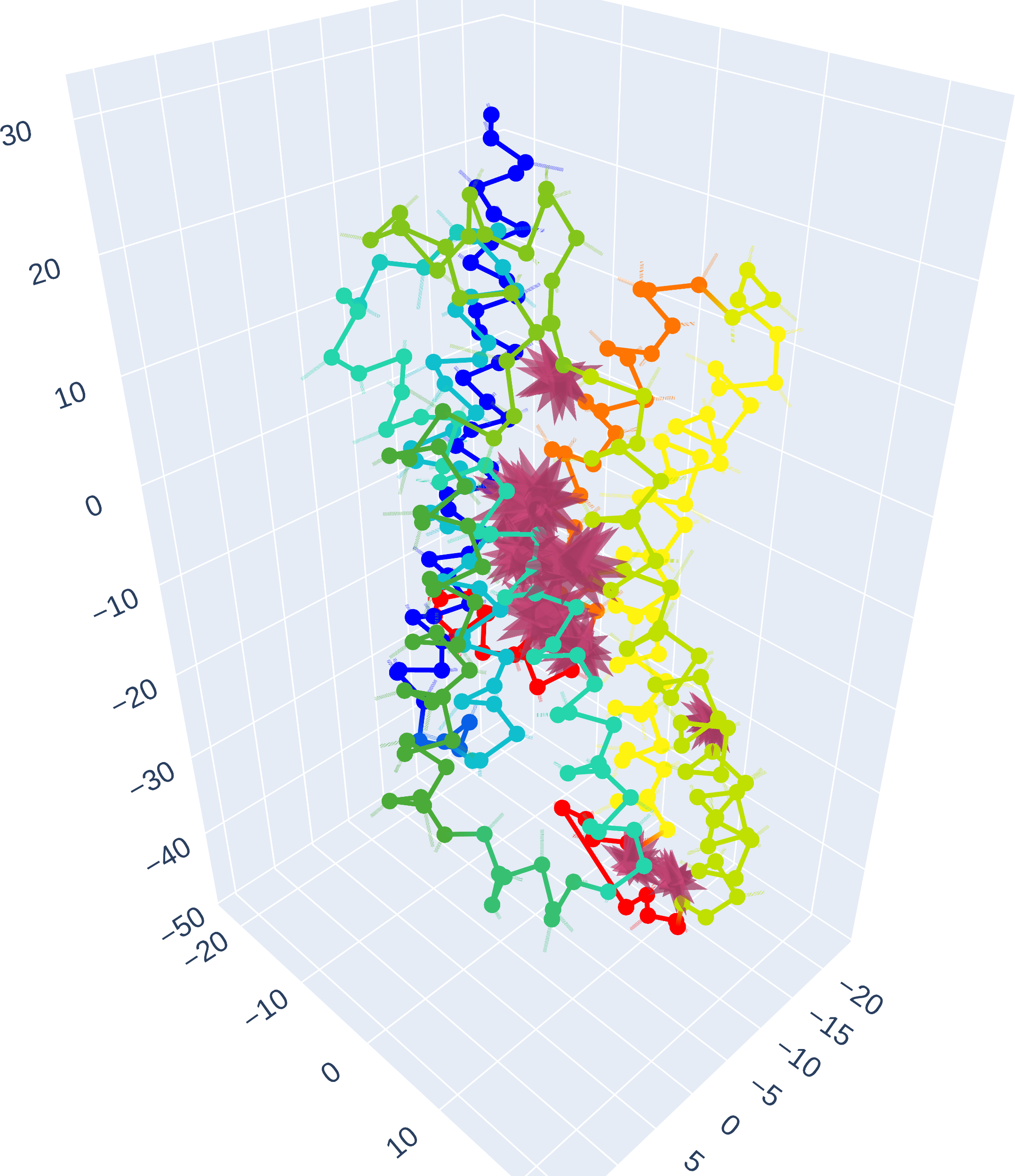
ADRB2 - Residues Interactions
CLICK ON IMAGE FOR INTERACTIVE REPRESENTATION
The model reveals significant attention to residue interactions centered around 7.46, 7.47, 7.50, and 7.53, which are part of, or adjacent to, the conserved NPxxY motif in class A GPCRs, crucial for stabilizing the receptor's active state and guiding conformational changes during activation [1,5].
The model also underscores the importance of residue 8.47, positioned in a pivotal hinge region between TM7 and H8 of the GPCR, associated with the receptor's transition into its active state [4,7].
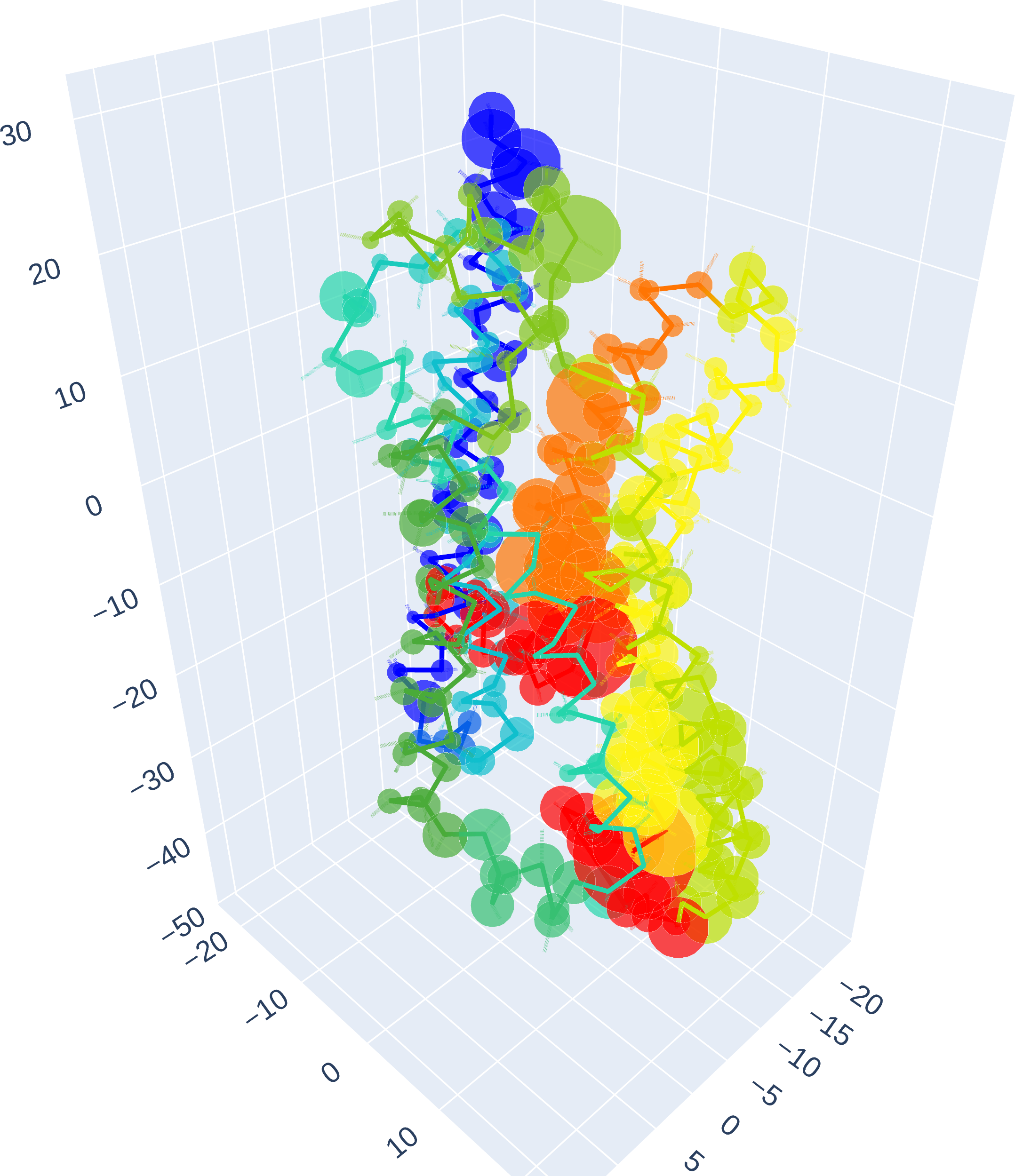
ADRB2 - Residues
CLICK ON IMAGE FOR INTERACTIVE REPRESENTATION
Similar to the Residue Interaction results, the model reveals significant attention to residues 7.49, 7.50, 7.51, and 7.52 (NPxxY motif [1,5]) as well as 8.47, positioned in a pivotal hinge region between TM7 and H8 of the GPCR [4,7].
Furthermore, we see 6.31, adjacent to 6.30, a key component of the D(E)RY motif in class A GPCRs, stand out. This motif, essential for receptor activation and regulation, maintains the receptor's inactive state through an ionic lock, which, when disrupted by ligand binding, triggers receptor activation and G-protein coupling [6,8].
References
| [1] | Injin Bang and Hee-Jung Choi. Structural Features of B2 Adrenergic Receptor: Crystal Structures and Beyond. Molecules and Cells, 38(2):105--111, February 2015. [ DOI ] |
| [2] | Michael R. Braden, Jason C. Parrish, John C. Naylor, and David E. Nichols. Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists. Molecular Pharmacology, 70(6):1956--1964, December 2006. [ DOI ] |
| [3] | Kuglae Kim, Tao Che, Ouliana Panova, Jeffrey F. DiBerto, Jiankun Lyu, Brian E. Krumm, Daniel Wacker, Michael J. Robertson, Alpay B. Seven, David E. Nichols, Brian K. Shoichet, Georgios Skiniotis, and Bryan L. Roth. Structure of a Hallucinogen-Activated Gq-Coupled 5-HT2A Serotonin Receptor. Cell, 182(6):1574--1588.e19, September 2020. [ DOI ] |
| [4] | Piotr Kossoń, Jolanta Dyniewicz, Piotr F. J. Lipiński, Joanna Matalińska, Aleksandra Misicka, Andrzej J. Bojarski, and Stefan Mordalski. Gαi-derived peptide binds the -opioid receptor. Pharmacological Reports, 75(2):465--473, 2023. [ DOI ] |
| [5] | Luciana M. Leo, Rufaida Al-Zoubi, Dow P. Hurst, Anna P. Stephan, Pingwei Zhao, Douglas G. Tilley, Elke Miess, Stefan Schulz, Mary E. Abood, and Patricia H. Reggio. The NPXXY Motif Regulates β-Arrestin Recruitment by the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, July 2022. [ DOI ] |
| [6] | G. Enrico Rovati, Valérie Capra, and Richard R. Neubig. The highly conserved DRY motif of class A G protein-coupled receptors: Beyond the ground state. Molecular Pharmacology, 71(4):959--964, April 2007. [ DOI ] |
| [7] | Berkay Selçuk, Ismail Erol, Serdar Durdaği, and Ogün Adebali. Evolutionary association of receptor-wide amino acids with G proteincoupling selectivity in aminergic GPCRs. Life Science Alliance, 5(10):e202201439, May 2022. [ DOI ] |
| [8] | Reiner Vogel, Mohana Mahalingam, Steffen Lüdeke, Thomas Huber, Friedrich Siebert, and Thomas P. Sakmar. Functional role of the "ionic lock"--an interhelical hydrogen-bond network in family A heptahelical receptors. Journal of Molecular Biology, 380(4):648--655, July 2008. [ DOI ] |